Wound Treatment
chuangmianzhiliao
Methods of wound repair
The basic way of wound repair is to fill, connect or replace the defect tissue with proliferative cells and stroma. Ideal wound repair, the tissue defect is completely repaired by the original nature of cells, in order to restore the original structure and function. However, the inherent proliferative ability of various tissues and cells in human body is different. If a certain tissue trauma cannot be repaired by the original cells, it will be replaced by the proliferation of other cells (usually fibroblasts). Although its shape and function can not be completely restored, it can still repair the wound (fibrous tissue scar healing).

Process of wound tissue repair
The tissue repair and wound healing of trauma go through three stages.
1. Inflammatory reaction
It starts immediately after injury and usually lasts for 3-5 days. The purpose is to resist foreign body invasion, destroy necrotic tissue and prevent infection, so as to lay the foundation for tissue regeneration and repair. The manifestations are: rapid contraction and thrombosis of small vessels to control bleeding; Vascular permeability and leukocyte exudation were increased to control infection; Fibrinogen exudates to prepare for the repair process.
2. Tissue proliferation and granulation
At 24-48 hours after injury, epithelial cells began to proliferate at the edge of the wound. A part of the basal cells of the epidermis separated from the deep dermis, thickened, divided and swam to the edge of the wound to form an epithelial bridge; Fibroblasts can contract the circumference of the wound edge (wound contraction) and make the wound edge close to each other. For wounds that cannot be covered by epithelial cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells and neovascularization together form granulation tissue, which can fill tissue fissures that cannot be epithelialized; The original blood clot, necrotic tissue, etc., can be enzymolysis, macrophage phagocytosis, absorption or discharge from the wound. Granulation tissue eventually becomes fibrous tissue (scar tissue), which is connected between the broken tissues to form the later healing scar.
3. Wound contraction, tissue regeneration and shaping period
This period began 24 hours after injury and lasted for as long as one year. The proliferation of cells and the formation of granulation tissue make the wound tissue repair initially. Since then, the amount, thickness and density of collagen have been changing in the wound. Collagen can increase the tension strength of scar tissue by increasing the density of covalent cross-linking between molecules, increasing the cross-linking with non collagen components, and changing the configuration of scar collagen fibers. If part of collagen and other matrix in the scar is transformed and absorbed, it can make the scar soften and maintain the tensile strength.

Types of wound healing
Primary healing
It refers to the wound healing with less tissue defect, neat wound margin, no infection, tight wound Union after self tissue adhesion or suture, and no or little granulation tissue. The typical wound is a surgical incision, and the wound after debridement and suture can also achieve this effect. The time of primary healing is short, the scar formation is less, and only a linear scar is left after healing.
Secondary healing
It can be seen in the wounds with large tissue defect, necrotic tissue, infection or delayed surgical debridement and suture. This kind of wound has a lot of necrotic tissue and obvious inflammatory reaction. Wound healing can only be achieved after infection is controlled and necrotic tissue is removed
Here we go. The healing time of secondary healing is long and the scar is large. SUBCRUSTAL healing is a special type of secondary healing. The blood, exudate and necrotic substance on the surface of the wound dry to form a dark brown hard scab. The secondary healing process under the scab is called SUBCRUSTAL healing. The healing time under the scab is longer than that without scab, because the epidermis regeneration needs to dissolve the scab first to grow forward.
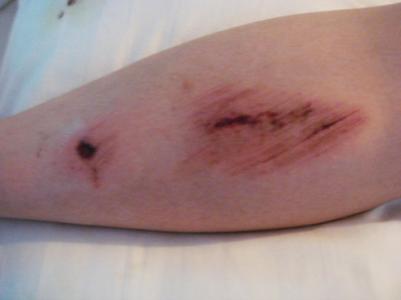
Factors unfavorable to wound repair
1. Infection is the most common obstacle in wound repair.
2. When there are foreign bodies or large hematoma in the wound, the healing time can be delayed, even complicated with infection.
3. Local major vascular injury or compression, or systemic shock, can cause insufficient blood perfusion of the injured tissue and delay the process of tissue repair.
4. Some drugs are not conducive to wound repair, slow wound healing and increase the infection rate. Common anti-inflammatory corticosteroids, anticoagulants, anticancer drugs.
5. suffering from systemic diseases is also not conducive to wound healing, such as malignant tumor, diabetes, no treatment, systemic malnutrition, etc.